We’re delighted that Andrea Powell, an Occupational therapist in Edinburgh has written a Blog for us about her experiences of being involved in group work with people who use AAC.
As a student occupational therapist, I worked part time as a support worker with an amazing lady Jennifer, (Jennifer is a pseudonym) Jennifer just happened to use an iPad to communicate. At this time I was about to commence my final year studies and was required to research and write a dissertation on a subject of interest. The lightning bolt of inspiration came when I, with Jennifer attended a weekly AAC user support group which was run and organised by a group of SLT’s.
The group was a wonderful resource that truly benefited the people who used it. I witnessed how much Jennifer valued spending time chatting with friends who also used an AAC device and who understood the unwritten rules of engagement. Such as patience while I set up my speech, don’t look at my screen while decide what I want to say etc. Her confidence in using different types of conversation grew while attending the group. It encouraged her to add to her already wide and variety vocabulary. As her support worker I also valued the opportunity to gain access to training on how to use her AAC and how I could provide better support to her.
I began reading around AAC and how people integrate of devices into their lives. I was however shocked to find that the wonderful group Jennifer attended was a rare occurrence for many users. The more I read, the more I realised that many users struggled to continue using an AAC device due to lack of support, access to trained professionals and most did not have wonderful resources like user support groups.
As an OT I was interested to explore the role in which I would play within AAC provision and found that as an OT I would be mainly providing support and advice on positioning, accessing devices and ergonomic type support.
However I felt that as an OT we have many more skills that didn’t appear to be to be getting utilised, within in my dissertation proposal I postulated that OT’s could expand their role within AAC to i) collaborating on assessments for AAC; ii) training on devices once they have been issued to users; and, iii) running and facilitating groups for AAC users and communications partners in the community.
OT’s are highly trained specialists skilled at understanding what is achievable and realistic for an individual. Occupational therapists assess individuals holistically in order to establish realistic and manageable goals which can be graded and adapted to suit the individual. Through the utilisation of appropriate grading of an occupation, a user can experience success and therefore less failure and frustration, ensuring the challenge is set at the appropriate level for the individual concerned (Park 2009).
Running and facilitating groups as a therapeutic tool is something that occupational therapists have been doing since the earliest days of the profession and groups are now utilised in many areas of practice (Howe and Schwartzberg 2001). By continuing this tradition, occupational therapists are well placed to take the lead in running and facilitating groups for AAC users, integrating social and community activities into the groups, for example, meeting in local shops to provide real life experience of interactions and, importantly, promoting the use of AAC to the general public. There are similar projects being attempted in Motherwell to increase the awareness of Dementia and make local businesses “Dementia friendly” (Shafii and Crockett 2013). Providing groups for AAC users not only enables them to learn how to use their devices, but also provides a support network of other users and communication partners.
I feel that if the skills of an OT were utilised in more than ergonomics then more positive outcomes could be seen for the user of AAC. I believe that if there were more OT’s taking on additional roles within AAC provision it could help reduce the pressure for SLT’s and the waiting lists to see SLT’s. It would also enable more users to be assessed to use AAC.
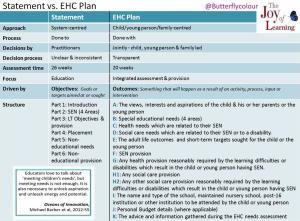
Part 1 highlighted how Talking Mats training can help improve your competency when consulting children and young people. In this part,we are grateful to Anita Devi, Education Consultant for illustrating the key differences between Statements and EHC plans. The changes have been implemented to enable individuals and families be active agents in their own lives rather than passive recipients of services.
Using Talking Mats as a communication tool enables practitioners to fulfil all stages of the assessment process and contributes to the development of the plan. The differences of the new system under the SEND reforms are illustrated in the table below (double click on the image to see it more clearly):
The local offer provides information on what services children, young people and their families can expect from a range of local agencies, including education, health and social care. Knowing what is out there gives more choice to individuals and to families.
The Local Offer has two key purposes:
1. To provide clear, comprehensive, accessible and up-to-date information about the available provision and how to access it, and
2. To make provision more responsive to local needs and aspirations by directly involving disabled children and those with SEN and their parents, and service providers in its development and review.
For children and young people, who struggle with communication, this can be quite a challenge. What is required is a communication tool that makes the process real and meaningful. Talking Mats breaks down the dialogue into bite-size chunks and gives the child or young person the space and time to meaningfully express his/her preferences and opinions.
Earlier in the year, Anita Devi & I published an article on “Listening to the learner :seeking the views of children and young people with communication difficulties.” It highlights the importance of creating a listening culture within the learning environment and using all modes of communication available. If we take the time to do this, the child or young person’s perspective will be taken seriously and the unique circumstances of each individual kept central to the process.
 Online training login
Online training login