We’re delighted that Andrea Powell, an Occupational therapist in Edinburgh has written a Blog for us about her experiences of being involved in group work with people who use AAC.
As a student occupational therapist, I worked part time as a support worker with an amazing lady Jennifer, (Jennifer is a pseudonym) Jennifer just happened to use an iPad to communicate. At this time I was about to commence my final year studies and was required to research and write a dissertation on a subject of interest. The lightning bolt of inspiration came when I, with Jennifer attended a weekly AAC user support group which was run and organised by a group of SLT’s.
The group was a wonderful resource that truly benefited the people who used it. I witnessed how much Jennifer valued spending time chatting with friends who also used an AAC device and who understood the unwritten rules of engagement. Such as patience while I set up my speech, don’t look at my screen while decide what I want to say etc. Her confidence in using different types of conversation grew while attending the group. It encouraged her to add to her already wide and variety vocabulary. As her support worker I also valued the opportunity to gain access to training on how to use her AAC and how I could provide better support to her.
I began reading around AAC and how people integrate of devices into their lives. I was however shocked to find that the wonderful group Jennifer attended was a rare occurrence for many users. The more I read, the more I realised that many users struggled to continue using an AAC device due to lack of support, access to trained professionals and most did not have wonderful resources like user support groups.
As an OT I was interested to explore the role in which I would play within AAC provision and found that as an OT I would be mainly providing support and advice on positioning, accessing devices and ergonomic type support.
However I felt that as an OT we have many more skills that didn’t appear to be to be getting utilised, within in my dissertation proposal I postulated that OT’s could expand their role within AAC to i) collaborating on assessments for AAC; ii) training on devices once they have been issued to users; and, iii) running and facilitating groups for AAC users and communications partners in the community.
OT’s are highly trained specialists skilled at understanding what is achievable and realistic for an individual. Occupational therapists assess individuals holistically in order to establish realistic and manageable goals which can be graded and adapted to suit the individual. Through the utilisation of appropriate grading of an occupation, a user can experience success and therefore less failure and frustration, ensuring the challenge is set at the appropriate level for the individual concerned (Park 2009).
Running and facilitating groups as a therapeutic tool is something that occupational therapists have been doing since the earliest days of the profession and groups are now utilised in many areas of practice (Howe and Schwartzberg 2001). By continuing this tradition, occupational therapists are well placed to take the lead in running and facilitating groups for AAC users, integrating social and community activities into the groups, for example, meeting in local shops to provide real life experience of interactions and, importantly, promoting the use of AAC to the general public. There are similar projects being attempted in Motherwell to increase the awareness of Dementia and make local businesses “Dementia friendly” (Shafii and Crockett 2013). Providing groups for AAC users not only enables them to learn how to use their devices, but also provides a support network of other users and communication partners.
I feel that if the skills of an OT were utilised in more than ergonomics then more positive outcomes could be seen for the user of AAC. I believe that if there were more OT’s taking on additional roles within AAC provision it could help reduce the pressure for SLT’s and the waiting lists to see SLT’s. It would also enable more users to be assessed to use AAC.
Thanks to Fiona Kane from the Alzheimer’s Resource Centre in Clydebank for sharing this lovely story about a visit to a man who had had a stroke. He was able to explain his views and take part in self management without realising it!
“Two of us visited a man who has aphasia. His wife is really struggling to communicate with him. She had been unable to attend the Talking Mats family training. I suggested the Talking Mats and they both agreed to try it out. I thought I would share it with you.
When we arrived the man was snoozing in the chair. He was extremely apprehensive when we first introduced the Talking Mats. However he quickly became very animated and we were able to tune into what he was saying.
A. asked him about gardening and he said he didn’t like gardening. He then invited us out to see his garden, was able to show us where he fell cutting a high hedge and indicated this was the reason why he had stopped working in the garden.
He told us he didn’t like religion and this was because his Mum was so strict with religion when he was younger.
He told us he really enjoyed photography and missed that. His wife is now going to buy a digital camera to help him continue with this.
He also told us that he enjoys listening to the radio but not radio 4 as there is no music.
His wife was absolutely amazed with the information her husband was able to communicate through the mats and he was able to express how much he enjoyed doing it. He was very animated and walked us out to the door.
It was a really amazing experience for both of us!”
Many thanks to Helen Paterson, one of our accredited trainers for this fascinating blog.
Now that Talking Mats is accessible in a digital format, the Talking Mats team are often asked ‘Can it be used on an eye gaze device?’ . Of course, for those who use eye pointing reliably, they can use a standard Talking Mat, but there are those individuals with whom we work with who may want to use their eye gaze device to use a Talking Mat, and who find the digital format more accessible. We would suggest that this is only done with a client who is already familiar with eye gaze , due to the extra effort required both to use eye gaze and to make decisions when using a mat. There are many other access methods with which you could use and access Talking Mats Pro, such as a head mouse, chin joystick or touch screen, but for this blog we will focus upon eye gaze. Here’s how we made it possible, and I am sure there may be other ways which we would love to hear about!
- To use Talking Mats Pro directly using eye gaze the person really needs to be calibrated on a device, and they require a level of calibration that is good enough that they are able to access a mouse emulator or Gaze selection on Tobii.
- You must ensure that the mouse emulation or Gaze selection features are set up and the person understands what the features are and what they mean e.g: left click, drag and double click.
- Open up Talking Mats pro on your account.
- You will need to select the topic, topscales and symbols for your client, as this will make it easier with less work for your client, although this is something you would do anyway as the person facilitating the mat.
- Now go through the question and the topscales as you usually would and explain them to your client.
- Select the first symbol and place it on the mat where they can see it.
This is where the 2 systems differ:
Mouse emulation: 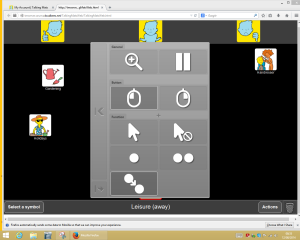
- Client first needs to open the mouse function menu by fixing his or her gaze on the small grey icon which will open the mouse menu.
- Client then fixates gaze to select the drag function (shown above)
- Then the client will select the symbol s/he wants to move by fixating on it.
- Once fixated, they symbol will ‘drag’ around the screen with the clients gaze. 5
- They will then fixate on a point to ‘drop’ it.
See Video
Gaze selection (Tobii):
- The client clicks selects drag function at the top of the Menu
- They then look at the symbol 3
- They then look where they wish to place the symbol.
This does require some more thinking on the side of the client as they need to look to where they want it to go and they are not just dragging it as they are in mouse emulation mode.
See video
For individuals who do not have a calibration good enough to use mouse emulation or gaze selection, it is a little more complex. A Talking Mat could be emulated from software such as The Grid 2 or Communicator, but it would not involve the software from Talking Mats Pro or dragging of symbols and moving them to where the person wants them to go.
Thanks to Helen Beltran for this thought provoking blog.
I am an Accredited Talking Mats Trainer and have just finished a great week of training in my local area, Inverclyde, Scotland. This was the first time I had given out symbol sets to everyone who completed the training. What difference did it make?
Everyone was able to see the symbol sets during the training and was really positive about the images and the design. I was concerned at the time that this would stop them really engaging with the process and individualising their mat. I was so pleased when they came back with videos that showed that they had selected the most appropriate options for their communication partner, they had removed those that were too abstract, they had thought about using photos, they had added symbols they had produced themselves. They had made the resources their own!
We talked about this as a group and all the participants felt that the symbol sets were going to allow them to get going with Talking Mats. They would then develop their bank of symbols, by making their own and buying further packs. Some participants told us that they felt having the symbol sets was allowing them to bring supportive colleagues on board who had not yet done the training and was combatting the negative attitudes of the vocal few who had the ‘not more work for us to do’ attitude!
They left with their symbol sets – full of ideas, not just about Talking Mats but about offering choice, hearing the individual’s voice, reducing vulnerability, relationship building and empowerment.
It has often struck me that some people are very much at home making picture resources and making their communication more visual, while others find it a real challenge. Is it reasonable for us to expect everyone to produce their own resources from scratch? Is the barrier to the use of visual communication the making of the resources, rather than the motivation to use them? On the other hand, is the making of the resources the only way to make sure that the supports meet the individual’s needs? What about the costs involved in buying in? Do those who are embracing visual communication need help with resources in order to spread good practice?
Food for thought?
We are delighted with the response to our new Talking Mats symbols. They created a real buzz at the ISAAC (International Society of Augmentative and Alternative Communication) Conference in Lisbon last week.” Its so good to see something fresh and engaging” , “These are awesome”
Over the past few years we have been looking at symbols in a new way and have used our specialist skills from clinical practice, research and language structure to underpin their development. These skills, in partnership with a leading comic artist, www.adammurphy.com , have enabled us to design our symbols, making sure that they are:
- Unique
- Attractive and fun
- Simple but represent concepts clearly
- Distinguish between concrete and abstract concepts
- Show full body, not stick figures
- Acceptable in terms of age and ethnicity
- Balanced between male and female
- Provide additional visual clues within topics to support understanding
Talking Mats does not require people to select and ‘name’ symbols – the important feature is that the symbols act as a support to hang meaning on. In this way people can understand and use the symbols to express their views .
To determine the size and colour of the symbols, we have used a pragmatic approach as follows:
A search of the literature showed that very little empirical research has been written about optimal symbol size and colour for different client groups. However several leading graphic and cartoon designers use yellow as this is easily recognisable, attractive and ethnically neutral e.g. Simpsons, Lego
- Our artist advised us that cool colours such as blue recede into the background visually whereas warm colours such as yellow stand out more
- We believe it is important to include text as this provides additional input for many people e.g. many people with dementia can read.
- From discussion with colleagues and reading learning disability literature we decided that Arial, san serif point 14 would be the clearest font
- We experimented with various sizes, using very large symbols on one dementia project. However we found that very large symbols are too distracting and limit the number of symbols that can be used on a mat. Following piloting with older people in care homes we determined that the optimal size for using with Talking Mats is 5.5 square cm.
- We ran focus group discussions with speech and language therapists, people with learning disability, people with aphasia and people with dementia. The focus groups presented participants with symbols of different styles, size and colours. The resulting responses plus our literature search led us to the current symbols in terms of design, size and colour.
- We then piloted the symbols in several settings including a day centre with adults with complex physical and cognitive disabilities, a care home with people with dementia and a secondary school with children with additional support needs. In all of these setting almost all participants were able to see, recognise and use the symbols appropriately.
- We made a conscious decision not use photos because photos often have too much detail on the one hand or conversely can be too specific… but that’s a topic for another blog!
We are constantly extending the range of symbols and are currently working on a resource for helping people to consider their Eating and Drinking. We are also working on providing additional visual clues within topics to help people understand concept more easily e.g. emotions are represented within a cloud border. e.g this poor guy is feeling guilty
We are really excited that our new symbols are now being used by 2 organisations outside the field of disability to help students and graduates reflect on their skills,strengths and weaknesses.
For further information click here
My name is Karin Torgny, I’m from Sweden. My background is in journalism and culture studies. I used to work in “The Development Centre for Double Exposure” for many years, and our mission was to improve and spread knowledge about violence against women with disabilities. My special interest during these years was AAC. Today I work for Unicef and in different projects on human rights issues.
A year ago I did my accredited Talking Mats training in Stirling, Scotland. Since then I have given my first course in using Talking Mats when talking about abuse and harm. It was a great experience and an opportunity to work with an enthusiastic group of women who were open and willing to communicate using symbols. They are all in an organisation working with girls/women with intellectual disability exposed to violence and oppression in the name of honour.
I think Talking Mats is a good tool when approaching difficult subjects and I hope to run more courses like this in Sweden in the future. Lately I was interviewed on the Swedish Radio and talked about the use and possibilities with Talking Mats when someone is exposed to harm and abuse.
For those who know Swedish (!), here is a link to that program, http://t.sr.se/1mxZv9W
I am also curious if someone else is doing something similar. If so I would be interested to know more. Send an e-mail to: karin.torgny@gmail.com
Have a look at how Talking Mats has been used in Scotland to support people with a learning disability to disclose issues of concern: Survivor Scotland
Talking Mats is fun! Whether you are sitting on the floor completing your mat or sitting at a small table, young children enjoy the fact that they can give information through multiple channels – Talking Mats is visual, auditory and tactile. It is an engaging tool to use when consulting children.They can express a view without words if they want to or they can have a conversation if they enjoy chatting. Watching a young child thinking and reflecting about where they place their symbol on the mat can be a humbling experience. Some adults still consider young children as incapable of expressing their views or opinions but in reality they can often express strong views about things and are very capable of grading their responses. Sometimes we just don’t take the time to ask them about the issues in their lives and free up some time to listen.
Talking Mats has created a specific Early years resource to make consulting young children easier. The symbols have been graded according to their developmental stage. When using the picture symbols it is important to remember:
- Most of the symbols in the Early years pack are concrete and you can quickly identify the shared meaning for example – “drawing”
- Others are concrete but have a broader meaning. An example of this is when asking about “eyes”
We have found that it is best to allow the child to interpret the meaning at their level so it maybe they have sore eyes; they don’t like their glasses or they have brown eyes. Try not to be too prescriptive when presenting the option to the child; a symbol can act as a jump off point capturing what fits for the child at the time. Just allow the meaning to emerge.
• The abstract symbols do need a bit more explanation because they ask about more complex concepts such as safety. The Early years pack asks about safety in relation to the road, physical safety and safety around others.
Asking about daily routines will give insight into how nurtured and cared for they feel. Let the child lead the discussion as much as possible.
Using visual communication is a great way to have a conversation with children in the early years and a good tool to involve children in decision making. Listening to the child’s view is essential for the GIRFEC process in Scotland and for co-producing Education Health care plans in England and Wales. Talking Mats has created a unique resource which is based on the “International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health – Children and Youth version” Talking Mats uses a framework which helps children to express themselves in a way they feel comfortable with. As adults we need to be able to facilitate the conversation.
We find that to realize the full potential of Talking Mats it is best to attend a Talking Mats course . The courses allow you to focus on your situation and how you can be creative and apply it in your own work,
We are frequently asked if Talking Mats can be used by someone who is blind and we usually say ‘not really as its essentially a visual tool’. However today I had to eat my words when I was interviewed by Ian Hamilton who is a BBC Scotland TV and radio reporter. Ian is totally blind and was accompanied by his guide dog – a very large but gentle German Shepherd called Renton. Here is a link about Ian and Renton
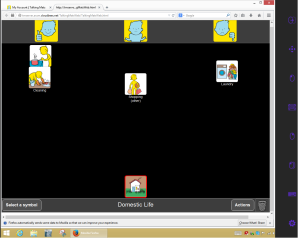
When Ian asked me to explain Talking Mats I guided his hand to the positioning of the 3 top scale symbols and then he immediately understood the layout of the top scale, the topic at the bottom of the mat, and where to place each option by touch. I simply explained each symbol, placed it in his hand and he did the rest. The topic was how Ian feels about Domestic Life and we had a lot of laughs about his dislike of shopping, laundry and cleaning. He explained that shopping was a nightmare for someone who is blind. He said that the dislike of laundry and cleaning showed that he was lazy – I think it’s pretty much what lots of people think!
However he was clear about a number of things that he feels very positive about, in particular his daily routine and his security, both of which are very important because of his blindness. Interestingly he said that his guide dog is clearly on the positive side of the mat, but not as a pet. A dog like Renton is not just a form of mobility, he’s also a fantastic companion.
Ian seemed to keep 1 step ahead of me and asked loads of great questions about Talking Mats as a thinking tool and its possibilities for other groups of people. He commented that, like inventions such as the typewriter and the phone, Talking mats is something originally intended for people with a disability, but which is now being used by people of all abilities to help them consider issues and then express their views.
Ian generously agreed to me writing this blog and using his photo.
The programme will be broadcast on BBC Radio Scotland : Business Scotland on 24th and 25th May
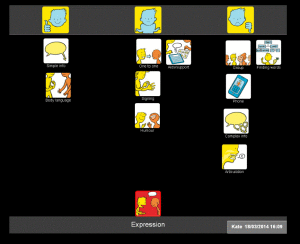
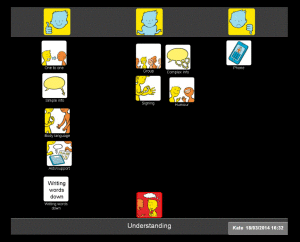
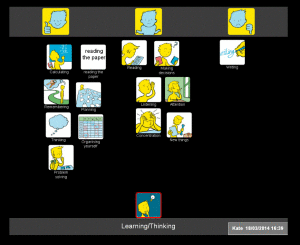
In the Health and Well-being resource, we have provided four sets of symbols to help people consider how they feel about their communication. Because communication is complex and often abstract, it can be particularly difficult for people to express their views about it, especially if they have existing communication difficulties. To make this easier, we have divided communication into four topics:
- Expression
- Understanding
- Learning and thinking
- Relationships.
In the following example, I show how each topic can be used to build up a picture of how someone feels about different aspects of their communication. I worked with Kate, a 42 year old woman who had a stroke which left her with severe expressive and receptive aphasia. She was able to communicate through vocalisations and gestures. She could sometimes draw or write down words and needed to point to ‘yes/no’ in order to reliably answer closed questions. Following discharge from hospital, I used Talking Mats with Kate to find out how she felt about her communication. I started with the ‘communication – expression’ topic and found that she felt that she was having lots of difficulties making herself understood, particularly on the phone and in group situations:
I then explored how Kate felt about understanding what people were saying to her. Kate was able to tell me that she found it easier to understand people on a one to one basis rather than in a group setting. She indicated that it really helped her if people used gestures or wrote things down. Her main difficulty was understanding people on the phone, and in fact she had stopped answering the phone altogether (see mat below).
We went on to do a mat about Kate’s learning and thinking. In this set, there are symbols which cover higher level language activities such as reading, problem solving and organisation. When we talked about these areas, Kate was able to tell me about the things she was finding most problematic, but could also identify some things that she felt she could still manage (such as calculations and reading newspapers).
I then asked Kate how she felt about communicating with different people in her life. This mat shows that Kate found talking to her husband and her parents (who lived quite far away) particularly difficult.
As a result of doing these mats, we were able to target the things that mattered most to Kate in relation to her communication, and came up with the following actions:
1. Kate felt that her husband needed support and information, so we spent time working with him, showing him the best ways to support Kate’s communication.
2. Because Kate’s parents lived quite far away, she could only contact them using the phone, which was very difficult. We worked on getting Skype set up so that Kate could communicate with her family using all the modes available to her.
By splitting communication into different sub mats, Kate was able to think about different aspects of her communication and identify the things that she found most challenging. Together we began to work out some ways to help her overcome her difficulties.
Use the communication symbols to find out what people want to work on and use a collaborative approach to establish some goals to work on in therapy. I used the original Talking Mats when I explored Kate’s communication with her, but you could do the same with Digital Talking Mats. Find out more about it here.
Within the Health and Well-being resource there are four symbol sets (health, looking after yourself, communication and leisure & environment). Within the ‘health’ set, there are three topics which can be used to help people express their views about different aspects of their health:
• Health
• Coping
• Mobility
I worked with Pete who had severe aphasia. Pete had a range of health problems, including epilepsy and high blood pressure. Pete found it very difficult to communicate with his GP, and usually relied on his wife to translate. This meant that not all of Pete’s health problems were addressed or discussed when he went to the doctor, and he often felt excluded from conversations at these appointments. Prior to one of Pete’s GP appointments, I used Talking Mats with Pete to find out how he felt about his health. During our discussions, Pete was able to tell me that he was worried about a number of issues, but he especially wanted to talk to his GP about his ears, as he was having a lot of pain and also had a ringing sensation in his ears which meant that he found it very difficult to concentrate, particularly when watching TV.
Pete took the photo of his completed mat with him to his next GP appointment and his GP used this as a focus for discussions. As a result, Pete was referred to an audiologist for assessment. His GP also spent time discussing Pete’s epilepsy with him and referred him back to the epilepsy specialist nurse who worked with Pete and his wife to improve their understanding and management of it.
Using Talking Mats helped Pete prepare for his GP appointment and also ensured that his GP focused on what was important to him. As a result, time was spent more effectively by all and Pete felt listened to and really participated in his GP consultation.
Use the Talking Mats ‘health’ symbols from the health and well-being resource to help people prepare for appointments with health professionals and manage their health more effectively.
 Online training login
Online training login