We are delighted to share a poster from Licenced Trainers Brid Corrigan and Libby Mills of NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde, and Student Speech and Language Therapist Heather Pollock, developed as part of an Impact Project with the University of Strathclyde.
The poster reports on an evaluation of the impact of Talking Mats training on clinical practice across several Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) in and around Glasgow. We were thrilled to hear the poster had been accepted at the Solving the Mental Health Crisis: Global Solutions Across the Lifespan Conference, held on Friday 21st June.
The project demonstrates how Talking Mats can be used by several members of the multidisciplinary team to build rapport and set goals with young people in both the inpatient and community CAMHS setting. A huge well done to everyone involved in the project for shining a light on how Talking Mats can help to hear the young person’s voice as part of their CAMHS journey.


This week’s guest blog, the first of 2 from the authors (Lois Cameron, Nikky Steiner and Luccia Tullio), describes the development process of a set of symbols aimed at supporting practitioners to reflect on the role of identity within their practice.
Every person has their own unique identity, just like they have their own unique fingerprint.
Identity is about how we see ourselves and how the world sees us.
Background
The Royal College of Speech and Language conference 2021 was titled ‘breaking barriers and building better.’ Professor Harsha Kathard from the University of Cape Town gave the keynote presentation and reflected on the key role understanding identity has in clinical practise, stating that ‘understanding identity is key to inclusion’. Secondly, she stressed that if we want to develop better services and support then ‘Turning the gaze to reflect on our positionality is central to change’ .Ash R et al (2023) in their editorial for the British Medical Journal highlight how interventions normally focus on single categories of social identity and ‘fail to account for the combinations of, or intersections between, the multiple social characteristic that define an individual’s place in society.’ They argue that ‘systems of care may consequently overlook overlapping systems of discrimination and disadvantage and exacerbate and conceal health inequities.’
The Development group
Following feedback from clinicians and people who use Alternative and Augmentative Communication (AAC) a working group was formed in March 2021 to explore the role of identity, diversity, equality and inclusion with in AAC practice.
Communication Matters and AAC networks within the UK advertised the group and 12 people responded. These people came from a range of organisations and had a range of lived experiences of diversity including people who use a communication aid to help them communicate. The work was funded by the Central London Community Health Trust and Talking Mats Ltd facilitated the meetings and the work
The group worked shaped the resource by reaching a consensus about the components of life that contributed to identity. In the end the group agreed on gender, sexuality, disability, race, neurodiversity, culture, family structure, voice, bilingualism, religion, mental health, personality, politics, intimacy, connecting with others and occupation. The process of developing the symbols was hugely helpful in unpicking what was actually meant by the various aspects e.g. voice. The original image for voice represented accents but the group discussion shaped the image to represent much more so the final image included a rainbow flag, a more general sound wave to represent tone, a Spanish word and an image to represent disability. As one group member said ‘my cerebral palsy is part of my identity. If I am having a voice I want to reflect that identity – I want a cerebral palsy voice’. Identity and the issues surrounding it can be emotive but the focus on the symbols helped contain the emotion and supported group members to listen to the perspective of others.
The whole iterative process of developing the resource and clarifying what the symbols should look like allowed the group to be clear about the individual meanings of abstract topics. This wider understanding was captured in a glossary to go alongside the symbols. For example, Identity has the following definition: Every person has their own unique identity, just like they have their own unique fingerprint. Lots of different characteristics make up our identity. This is what makes us different from other people. Sometimes we may share some of these characteristics with other groups of people, which can also be part of our identity. Identity is about how we see ourselves and how the world sees us.
Equality, Diversity and Inclusion: a visual framework to support the exploration of Identity within practice.
The resource is seen as a support for constructive reflection by practitioners on identity and allows them to consider the different aspects of their patients’ lives that may impact on their interventions. The final Talking Mats symbols have the suggested top scale of ‘I considered a lot’, ‘I considered a bit’, ‘I have not considered yet ‘. It could be used individually or by a team as a group discussion tool.
As the resource uses the Talking Mats framework, it is recommended that practitioners have completed their Talking Mats foundation level training
If you are interested in completing Talking Mats Foundation Training, you can see the training options in our shop here.
References
Kashard H 2021 Keynote breaking barriers and building better The Royal College of Speech and Language conference.
Ash Routen, 1 Helen-Maria Lekas, 2 Julian Harrison, 3 Kamlesh Khunti1,2023 Interesectionality in health equity research BMJ 2003 https://www.bmj.com/content/383/bmj.p2953
Our thanks for this blog go to Olivia Ince, Talking Mats Licenced Trainer and Speech & Language Therapist. This blog post reflects on the use of a Talking Mat with a Thinker called M who speaks English as an additional language. The Listener in this Talking Mat is Jono Thorne who is a colleague of Olivia. Jono did this Talking Mat for his video as part of a Foundation Training course run by Olivia.
M is a young adult who came to the UK as an unaccompanied asylum-seeking child. M is from a country in Central Africa and speaks a language which is not widely spoken outside of the region. Accessing interpreting and translation services in the UK for their native language is very difficult and M has therefore had difficulties learning English. This means the people around M often have difficulties finding out M’s views, which is why Jono thought a Talking Mat could be an invaluable communication tool for M.
M already uses some visual support, for example hand gestures and using objects such as food items when having a conversation in the kitchen. The people around M are unsure what M’s level of comprehension is in English and therefore they make adaptions such as simplifying their language. M’s expressive language in English is typically the use of one- or two-word utterances and yes/no responses.
To see if M would be able to engage with the Talking Mat process, Jono chose a simple topic to start with and one which he knew would interest M: food. The Top Scale used was like/unsure/ don’t like. Jono noted that M quickly understood the concept of the Talking Mat and the visual element seemed to support M’s understanding. The Talking Mat process including the side-by-side listening also facilitated rapport building.

Jono noticed that M was decisive and seemed certain about their placement of the option cards. The Talking Mat helped M to share their views on a larger number of items than would likely have been possible via a verbal conversation. M also joined in with the recap of their Talking Mat as part of the review and reflect by reading out the Option cards with Jono, which meant M was even more involved with the process.
There were a couple of difficulties for M during the Talking Mat process: the blanks and the option to change where the Option cards were placed. Jono tried to explain these steps using simple language but M did not appear to understand these concepts due to their level of comprehension of English. As M had seemed sure of their initial placement of the Option cards and they joined in with the recap, Jono felt that the Talking Mat was an accurate reflection of M’s views that day. Continuing to model these steps to M will likely help them to develop their understanding of these parts of the Talking Mats process over time.
Jono reflected on how useful it was to now know which foods M likes and doesn’t like. He also reflected on the potential future use of Talking Mats with M on more complex topics and to facilitate participation in decision-making now that it’s clear M understands how a Talking Mat works.
If you are interested in completing Talking Mat Foundation Training, you can read more about it here.
Our thanks for this blog go to Deborah Little, Speech and Language Therapist; Clinical Lead for AAC & Total Communication (Children and Young People) NHS Dumfries and Galloway.
“Can we do a Talking Mat today Deborah? This is the question I am asked as soon as I enter the Learning Centre in one of our local schools by an enthusiastic 8 year old who has been exploring what completing a Talking Mat (TM) is all about this term. While we are in the early stage of this school’s TMs journey, the impact of embedding the approach into the fabric of how Children and Young People (CYP) are supported to communicate in school is already proving transformative.
Article 12 of The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC) guarantees children the right to express their views and opinions freely in all matters affecting them. The responsibility of ensuring children experience this right is also underlined in NICE guidelines (2022) that state: “Education, health and social care practitioners should always: put the life goals and ambitions and preferences of the disabled child or young person with severe complex needs at the centre of planning and decision making.”
Working with my teaching colleagues within one Additional Support Needs (ASN) setting this year, we reflected on how effectively the CYP were able to give their views and how consistently these views were acted upon in meaningful ways. We felt that this was an area we really wanted to improve upon and specifically we wanted to explore the following key questions in our minds:
- How can we support CYP’s understanding of their right to give their views and opinions? We reflected that for some CYP, their experience of being able to do this was very limited and that their understanding of using a TM was not yet at a stage where they were able to represent their views. We therefore wanted to prioritise finding out what helped these CYP to use TMs with understanding.
- How can we support CYP to know that they can tell us they aren’t happy about something? We reflected that during ‘Emotions Works’ discussion times many of the CYP routinely shared that they felt ‘happy.’ It was rare for the CYP to talk about unhappy feelings. We felt worried that the CYP often gave responses that they felt would be ‘right’ or pleasing to adults.
- How can we ensure we create a culture of prioritising time and space for CYP to share their views, opinions and ideas? We thought about opportunities throughout the school week that would create space and motivation for the CYP to engage with TMs. We wanted to achieve a feeling of TMs being integral to the everyday, as opposed to a sporadic ‘add on.’
To answer these questions, we agreed on the following key change ideas to implement and evaluate:
Developing understanding of the Talking Mats process linked with familiar learning opportunities.

Dynamic Assessment is an approach familiar to those working with CYP who use Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC). Adapting activities dynamically, being responsive to CYP’s progress, allows progressive skill enablement. Together with teaching colleagues, we applied this thinking to helping the children use TMs with understanding. If we had tried having a conversation using TM only a couple of times, our evaluation could have been that TMs wasn’t yet a tool we could use because for example, the CYP were putting all their symbols into the ‘I’m happy with this’ column only. Instead, we thought “OK, that’s where the CYP are now, let’s give them opportunities to practise engaging with this new tool and time to develop using the approach with understanding.” Put another way, we prioritised another key concept within the field of AAC: we Presumed Competence. We believed that the CYP had the ability to share their thoughts, feelings and ideas if we introduced TMs gradually, linking with the activities above, that were tangible and familiar to the thinkers.
Consciously modelling that is OK to have negative feelings and opinions.
When a CYP is learning what might be possible in terms of communicating with AAC, best practise is for supporting adults to model the AAC. This means, adults ‘use AAC to teach AAC.’ We show CYP that we highly value the AAC and want to use it too. We use it in real situations, modelling vocabulary to help CYP understand the symbolic vocabulary and how they can begin to use it too. When helping the CYP understand how TMs could help them express a wider range of emotions, we tried out using this approach. Now and again, supporting adults would share with the CYP how they were feeling about things using TMs and would include negative feelings.

One CYP had a memorable response to my sharing that I was feeling “not happy” with my cat. The CYP’s eyes widened and he became instantly animated, using his AAC to ask “cat..bad..what?” I was able to explain that my cat had been scratching my carpets and I was feeling upset about this. The CYP then used his AAC to say “cat…dig!” He pointed at the ‘not happy’ symbol in the Talking Mats top scale, jointly sharing his attention to this symbol and understanding of what this meant with me. The next week, we used TMs to ask this young person about a social group he had attended. For the first time, we noticed him ‘swithering’ across his top scale while making his choices. Also for the first time, I was confident that he shared his authentic feelings with me. I reflected on the power of modelling and normalising feelings that are ‘not happy.’
So, where are we now? The key themes from our findings after a year of using TMs as described above are:

In summary, using TMs in this setting has all supporting practitioners in agreement that it is not only important to listen to CYP when we know they might be having a tough time; we need to create space to listen all of the time, week to week, with authenticity and without agenda. The principles regularly used within AAC practice of: modelling, presuming competence and dynamic assessment have been effective in supporting more children to be able to experience their UNCRC Article 12 Right, more of the time and with increased understanding and confidence.
References
- UN Convention on the Rights of the Child – UNICEF UK
- NICE Guidelines [NG213] (2022) Disabled Children and Young People up to age 25 with severe complex needs: integrated service delivery and organisation across health, social care and education.
- Emotion Works www.emotionsworks.org.uk
- Daneshfar, S and Moharami, M (2018) Dynamic Assessment in Vygotsky’s Socioculturaly Theory: Origins and Main Concepts. Journal of Language Teaching and Research 9(3):600
- Donnellan, A (1984) The Criterion of the Least Dangerous Assumption. Behavioural Disorders, 9 (2), 141-150
- Sennott, Light and McNaughton (2016) AAC Modelling Intervention Research Review. Research and Practice for Persons with Severe Disabilties 41 (2)
Do you work with people with intellectual disabilities and / or autism?
Researchers at the University of Hertfordshire have been working with Talking Mats to develop a range of symbols to help people with intellectual disabilities and/or autism to communicate symptoms of long Covid. It is hoped that these symbols will help facilitate conversations and improve accessibility to long Covid service pathways and improve health outcomes.
There are three topics that have been developed:
- Symptoms – This Topic uses a suggested Top Scale of I have / I sometimes have / I don’t have. Options in this topic include heart going fast , dizziness , brain fog.
- Mood – This Topic uses a suggested Top Scale of This is me / This is sometimes me / This not me. Options in this topic include frustrated, not interested, confident
- Getting Help – This Topic supports you to discuss how supported the individual feels and where their key supports are coming from. A suggested Top Scale is Going well / Unsure / Not going well. Options in this Topic include GP, online/phone support, specialist team.
This Talking Mats resource was developed in partnership with a group of people with intellectual disabilities and people with autism alongside a range of health professionals. People who had lived experience of long Covid were also involved in the group.
Participate and use the resource
We would like to hear from a wider cohort of practitioners working with people who have learning disabilities. For example, nurses, speech and language therapists and occupational therapists. We want to know if there is a need for this long Covid Talking Mats resource. This resource can also be used where long Covid has not been formally diagnosed but you want to listen to the person with a learning disability and hear about their experience of their long-term health condition.
If you would like to participate, and meet the following criteria, we would love to hear from you.
Criteria:
1. Have completed Talking Mats Foundation Training course.
2. Work in a setting supporting people with intellectual disabilities and/or autism.
If you would like to get involved, please complete the following survey by the end of April 2024.
Click here for the Long Covid Survey
Please note that should you consent to be involved in this project, your information will be shared with the University of Hertfordshire.
The team will be looking for feedback by the end of July 2024 and you will be asked to fill in a short survey for each Talking Mat that you complete . This survey will be sent to you alongside the long Covid resource.
If you have any questions about this, please do not hesitate to contact info@talkingmats.com
Thanks to Julia Pollock, Highly Specialist Speech and Language Therapist (SLT) from the REACH team in Perth for the second part of this latest guest blog sharing information about our exciting project, which has aimed to produce a resource to open up conversations with young people about sex.
By far, the most impactful feedback we’ve had during the pilot stage of this project has come from the social worker of the young person who I initially created the resource for. She was very keen to share with us that she had used the resource with the young person (two years on) and said it was ‘absolutely fantastic – I can’t tell you how good it was’.
Using the updated version, she was able to revisit the young person’s sexual knowledge and understanding and found that he was able to understand and have adult discussions around much more complex and abstract concepts than he had previously. The concepts included consent, contraception and sexually transmitted diseases. This was in stark contrast to his initial bewilderment when we first introduced the resource to him!
This has been a perfect case study for us as the resource has been used to support this young person through their entire criminal justice journey and through their sexual development into adulthood. The first draft had been used to initially gather information about his sexual knowledge and understanding in addition to information about the harmful sexual behaviour. It was later used to guide and support his sex education.
Now we have come full circle, with social work using the updated version of the resource to reflect on the past, helping him to understand his sexual development and to help guide his understanding around navigating future adult relationships in a safe and appropriate way.
‘He is ‘a confident, happy young man with the knowledge he needs for the future. There has been a lot of repair to his sense of self and moving from describing himself as a “monster” to understanding that he had a lack of knowledge and didn’t have the skills to navigate his sexual development safely. He is now able to accept his sexual feelings as being a “normal” part of development and to think how these can be expressed safely. His ability to integrate knowledge/reflect has been remarkable!‘
‘Importantly, we have also worked hard with the family to help them to accept him developing into a young adult with sexual feelings and the need to have access to peer relationships.‘
‘The Mat was brilliant in bringing all this together and providing the scaffolding to have these discussions with him.’
As a speech and language therapist, this process has been such a fantastic learning experience. It has been a joy and a privilege to work together with our social work and Talking Mats colleagues to create what will hopefully become an invaluable and essential resource in this field.

We are hosting an Advanced Webinar on the 5th of February 2025, 1.00pm to 3.30pm that is open to all trained Talking Mats practitioners working in this field.
Inspired to think about Talking Mats Foundation Training? Find out about all the options we have available here.
When this blog from Janie Scott, a Talking Mats Licenced Trainer with Perth and Kinross Council came in I was a bit stumped. There was a lot that I wanted to highlight but I didn’t want to focus on one thing and detract from others:
- The importance of understanding and applying the Talking Mats framework allowing conversations on topics not covered by our resources.
- Demonstrating how Talking Mats can enable the voice of the child to be heard, upholding Scotland’s Promise to care experienced children, young people, and families.
- A model for embedding Talking Mats in a service.
I decided to go with everything. In 2 parts.
Part 1
Talking Mats; UNCRC, the Promise and hearing the thinker:
Janie Scott, (Highly Specialist SLT Perth & Kinross Council)
Scotland is currently progressing with the incorporation of the United Nations Conventions on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC) through the UNCRC (Incorporation) (Scotland) Bill.1 The UNCRC, article 12, states that, ‘children have the right to give their opinions freely on issues that affect them. Adults should listen and take children seriously.’
Talking Mats enables rights-based participation for children, allowing them to form and express views freely. It allows others to understand the issues and, as stated above, have those views taken seriously 2
The ‘voice’ of the child is central to The Promise3. Talking mats should be considered the ‘scaffolding’ to enable a voice to be heard.

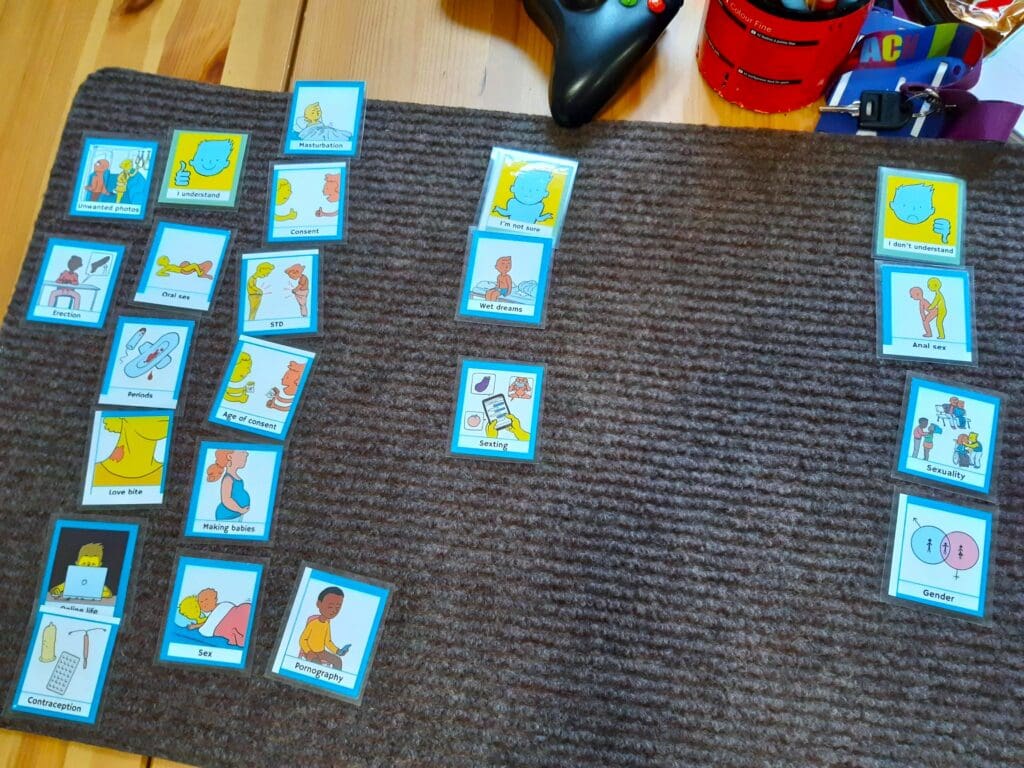
Last year I rolled out Talking Mats foundation training to Social Workers and Senior Social Care Officers working within Services for Children, Young People and Families, in Perth and Kinross Council. Fundamental to Talking Mats is the framework; the ability to use an appropriate top scale, open questions, silence and pass control to the thinker. Having demonstrated the importance of the framework in the training, we then went on to develop symbol sets specifically related to the work of the Social Work teams. These covered a wide range of topics including:
- sleep
- becoming a foster family
- contraception
- sexual knowledge
- contact arrangements,
- behaviours that adopted children think might be difficult to deal with
- grief
- school life
- triggers (related to drugs and alcohol)
I was privileged to hear several reports of how Talking Mats had allowed the voice of the children and young people to be heard which had a direct positive impact on their lives. Here are two powerful examples from a parent and a social worker.

Parent
” I have really enjoyed using Talking Mats. It lets me see everything in an organised way. I really like that. It has also shown me the progress I have made; I have found using an advocate really useful in the past but I don’t need to use an advocate any more as I feel more confident. I used to struggle with making decisions but this mat made me realise that I make decisions all the time and they are not wrong decisions.”
Assessing Social Worker for Kinship Care
“As part of my role, I need to find out information from teenagers on how they feel their kinship placement is going. Typically I find that many teenagers give one word answers or sometimes they tell me what they think I want to hear. Talking Mats has been useful in my work in allowing teenagers to open up. It has also been useful with children who have English as an additional language. The children did speak English, but it made it easier to get their ‘story’ from them.
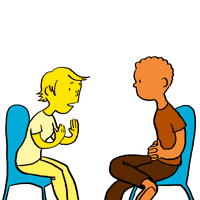
“There was one particularly quiet and reserved teenage boy who was reluctant to share information. The Talking Mat allowed him to tell me much more than when I had initially questioned him. Through the Mats we were able to distinguish the difference he felt between living at home and living with his kinship carers. The Talking Mat enabled him to express that his kinship carers were open to having discussions with him and talking about his worries whereas his Mum did not want to talk about his worries. this was something that I was able to support him in sharing with his Mum as part of the plan for him to return home.“
To uphold Article 12 services must be proactive in creating opportunities to listen to the voice of the child. Talking Mats is enabling the voices of children, young people and families to be heard in Perth and Kinross. This voice is influencing key decisions in their lives across a variety of forums including the Children’s Hearing System, Kinship Panels, and Child’s Plan Meetings.
- Children’s rights legislation in Scotland: quick reference guide – gov.scot (www.gov.scot) ↩︎
- Can Scotland be Brave – Incorporating UNCRC Article 12 in practice – gov.scot (www.gov.scot) ↩︎
- Foundations of the promise – The Promise ↩︎
Talking Mats Director, Margo MacKay, will be presenting with Laura Lundy, Professor of International Children’s Rights, QU, Belfast on Wednesday 1st of November, 2023 at NHS Education Scotland webinar; ‘The voice of the infant and child; rights- based participation for children and young people’
For more details please see the NES website.
Read ‘Can Scotland Be Brave, Incorporating UNCRC Article 12 in practice here
Talking Mats: developed in Scotland, embraced world wide with close working relationships in Japan, Sweden, Australia and New Zealand, but can the framework be adapted to reflect different approaches to communication that these diverse cultures embody? Victoria Mardell’s discoveries offer a fascinating insight into differences between Western communication and that of the Māori culture showing that the Talking Mats framework can be a cross culture communication tool.
Using Talking Mats in Te Ao Māori (The Māori World)
A Non-Māori SLT’s collaborative journey to deeper understand whether the Talking Mats process is culturally responsive to Māori
My Project
Working for the Aotearoa New Zealand Ministry of Education, I was approved to undertake a project which would investigate the suitability of Talking Mats to capture child voice.
A key part of this project was to review whether Talking Mats were culturally responsive to Māori and reflective of Māori worldview and if not, whether they could be altered accordingly.
This led to a rewarding journey for me as a non-Māori practitioner as I was able to collaborate with Māori colleagues and improve my cultural awareness. I got to experience Māori ways of gathering and acquiring information and I came away with new perspectives, which have shaped my practice.
Information Gathering: Learning About and Holding a Wānanga
To gather the information needed, it was suggested that I hold a wānanga. The word ‘wānanga’ would loosely translate as a “forum” in English. However, a more accurate description would be a collaborative process which involves engaging, sharing, and reflecting, with space for all viewpoints. A wānanga would often lead to the creation of new knowledge and decision-making.
This was my first experience with a wānanga and whereas Western ways of acquiring knowledge would likely have placed myself as an “expert”, seeking “feedback”, the wānanga was an unhurried deep discussion, in which all participants were partners, collaborating on an important subject.
Findings
There was overall agreement that Talking Mats are a good fit with Te Ao Māori.
Talking Mats were seen as a good way to promote Mana Motuhake (self-determination) and whakamana (giving prestige to children and their families).
Te Ao Māori (the Māori worldview) is strengths-based and the wānanga participants thought Talking Mats was a good fit with this approach.
Some considerations were discussed:
Codesigning the top scale: Participants discussed that concepts such as “going well” “not going well” are Western and that if a Talking Mat was used in a Māori kura (school), or with a Māori whanau (family), then categories might need to be adjusted or changed. This could be done via discussion and collaboration.
Māori colleagues have also shared some ideas with me for potentially suitable top scales:

(Sonja Macfarlane, 2021)
The key point was the importance of collaborating on the top scale rather than having this pre-determined before delivering the Talking Mat.
Being mindful about predetermination: Participants discussed how a practitioner turning up with a Talking Mat and a set of visuals might be seen as pre-determination and this could lead to discomfort and resistance. It would be more helpful if the practitioner facilitated a discussion, with the use of drawing visuals ‘on the fly’ as well as using the Talking Mats visuals. In practice this could look like a more collaborative process, with a greater input from the thinker in the early stage of the mat, rather than just at the end.
Action points may be strength-based rather than deficit-focussed: We discussed how there is a tendency in Western thinking to set goals or action points around improving things which the thinker has identified as not going well. However, in keeping with a Māori worldview, actions points might be to do more of what you already like, or to mentor others. We need to be careful that as practitioners, our unconscious bias is not inadvertently encouraging the thinker to focus on areas they have rated negatively.
Practice Example and Changes to my Practice
During the wānanga my former colleague, a Māori SLT, shared an example of a Talking Mat she had done about how a student wanted to participate in kapa haka (group performance of Māori dancing and chanting).
The SLT created her own visuals to reflect the kapa haka process. During conversation the SLT and student discussed how she could fatigue easily so the SLT drew an option to sit or stand. The action point was for the student to participate in waiata a-ringa (action song), with an option to sit if fatigued.

The process of considering Talking Mats through a Te Ao Māori perspective has changed my practice and I am grateful to my Māori colleagues for their time and insights. I am now more mindful when reviewing a Talking Mat, to make sure the action points are coming authentically from the thinker. I am also a lot more collaborative in the visuals and top scale of the Talking Mat. I have found that practising with more collaboration has led to better relationship building and more in-depth conversations.
Mauri Ora
Thank you to Victoria for her work on this blog. If you have any questions about this please contact us on info@talkingmats.com
Download and print top scales.
For users of Talking Mats getting your top scales right is a key part of the process. The sight of Matty with thumbs up / thumbs down / shrugging is a familiar one. It is our ‘go to’ top scale image, attached to our symbols in every resource you order. However, since the launch of our new digital resource where there is a choice of 16 top scales our TM community has been asking for the equivalent in card format.
So here it is:
If you are trained and have an account on the website you can download and print 16 different top scales to suit the conversations you are having and the thinkers you are having them with.
Before you all rush off to print, laminate and chop it is probably worth pausing to think about the top scale and how important it is in the Talking Mats framework. Making sure the top scale matches the question is vital to the conversation; for example if your topic is Self Care and the purpose is to find out if anything is causing a problem it is more appropriate to ask if someone is ‘managing / not managing’ rather than whether the task is ‘very important / not important’. The focus of the conversation becomes whether or not the Thinker can carry out the activity allowing for practical steps to be put in place to support them.

The midpoint of all top scales is included as we find it allows for indecision, an everyday part of the process of making decisions and forming opinions. Some people do struggle with too much choice however, and the top scale can be presented with just the 2 opposing points on the scale.
The printout includes top scales for our Advanced sets; ‘This is Me / This is not Me’, (Keeping Safe), ‘Sorted / Not Sorted’ (Thinking Ahead), and ‘Safe / Not Safe’ for our new Youth Justice resource, as well as options without thumbs and one that uses stars instead of Matty.

We know this new print out will be very useful to many of you when you plan your Talking Mats sessions and if you have any other top scales that you think could be added please let us know!
The printable top scales document can be found in the Shop if you are Talking Mats trained and you log into your account on the website
Read more about Top Scales https://www.talkingmats.com/when-is-a-talking-mat-not-a-talking-mat/
Many thanks to Peter Just, Head of External Affairs, RCSLT and Padraigin O’Flynn, External Affairs Assistant, RCSLT for this blog describing the newly launched UK-wide RCSLT Survey, which includes free Talking Mats resources to support those with communication difficulties to have their voices heard.
Like many of you, the Royal College of Speech and Language Therapists (RCSLT) has been worried about the impact of COVID-19 on people with communication and swallowing needs. Based on what we’ve heard from our members, service user organisations and service users themselves we’ve been very concerned about how the UK-wide lockdown (March-June 2020) affected people’s access to the speech and language therapy they and their families and carers need.
To help us understand the issue better and to inform our response, we’ve just launched a UK-wide survey. Following consultation with service user organisations, the three key questions we’re asking are:
- How did lockdown affect your speech and language therapy?
- What impact did this have on you?
- What are your thoughts about the future?
From the start, we were clear: we wanted the survey to be as accessible as possible to as many people as possible, no matter how they communicate and no matter what their communication preference is. Over the past couple of months, we’ve worked with members to produce the survey in a range of accessible formats.
We’re particularly delighted that one of those formats is Talking Mats – and we’re very grateful to Lois and Laura for all their advice and support . As you will know better than anyone, the mats will enable people to give us their views and tell us how they’ve felt and are feeling. We are delighted the mats will provide people with the means to self-advocate – this will add a richness to the survey findings that they might otherwise lack.
We’ll be working with service user organisations to promote the survey to their networks. But we’d also really like your help too. Please share the survey and encourage as many people as possible to fill it out. The more voices we hear, the more stories we collect and the more responses we receive, the greater the impact of the survey findings will be.
Those findings, which we hope to publish early in the New Year, will be used to influence Governments, Parliaments and Assemblies across the United Kingdom. The case that will be making to ministers, officials and parliamentarians – that people must have access to the speech and language therapy they need – will be all the stronger for it being based on service users’ lived experiences. The very powerful testimony that the mats will provide will strengthen that case even further.
The survey is open until 5pm on Friday, 8th January 2021 and you can find more information about it here:
https://www.rcslt.org/learning/has-coronavirus-affected-your-access-to-speech-and-language-therapy
We hope you find the mats useful and if you had any queries or wanted any more information, please let us know. We look forward to working with you to help make a difference to the lives of people with communication and swallowing needs.
Peter Just, Head of External Affairs, RCSLT
Padraigin O’Flynn External Affairs Assistant, RCSLT
 Online training login
Online training login 




