We are delighted with the response to our new Talking Mats symbols. They created a real buzz at the ISAAC (International Society of Augmentative and Alternative Communication) Conference in Lisbon last week.” Its so good to see something fresh and engaging” , “These are awesome”
Over the past few years we have been looking at symbols in a new way and have used our specialist skills from clinical practice, research and language structure to underpin their development. These skills, in partnership with a leading comic artist, www.adammurphy.com , have enabled us to design our symbols, making sure that they are:
- Unique
- Attractive and fun
- Simple but represent concepts clearly
- Distinguish between concrete and abstract concepts
- Show full body, not stick figures
- Acceptable in terms of age and ethnicity
- Balanced between male and female
- Provide additional visual clues within topics to support understanding
Talking Mats does not require people to select and ‘name’ symbols – the important feature is that the symbols act as a support to hang meaning on. In this way people can understand and use the symbols to express their views .
To determine the size and colour of the symbols, we have used a pragmatic approach as follows:
A search of the literature showed that very little empirical research has been written about optimal symbol size and colour for different client groups. However several leading graphic and cartoon designers use yellow as this is easily recognisable, attractive and ethnically neutral e.g. Simpsons, Lego
- Our artist advised us that cool colours such as blue recede into the background visually whereas warm colours such as yellow stand out more
- We believe it is important to include text as this provides additional input for many people e.g. many people with dementia can read.
- From discussion with colleagues and reading learning disability literature we decided that Arial, san serif point 14 would be the clearest font
- We experimented with various sizes, using very large symbols on one dementia project. However we found that very large symbols are too distracting and limit the number of symbols that can be used on a mat. Following piloting with older people in care homes we determined that the optimal size for using with Talking Mats is 5.5 square cm.
- We ran focus group discussions with speech and language therapists, people with learning disability, people with aphasia and people with dementia. The focus groups presented participants with symbols of different styles, size and colours. The resulting responses plus our literature search led us to the current symbols in terms of design, size and colour.
- We then piloted the symbols in several settings including a day centre with adults with complex physical and cognitive disabilities, a care home with people with dementia and a secondary school with children with additional support needs. In all of these setting almost all participants were able to see, recognise and use the symbols appropriately.
- We made a conscious decision not use photos because photos often have too much detail on the one hand or conversely can be too specific… but that’s a topic for another blog!
We are constantly extending the range of symbols and are currently working on a resource for helping people to consider their Eating and Drinking. We are also working on providing additional visual clues within topics to help people understand concept more easily e.g. emotions are represented within a cloud border. e.g this poor guy is feeling guilty
We are really excited that our new symbols are now being used by 2 organisations outside the field of disability to help students and graduates reflect on their skills,strengths and weaknesses.
For further information click here
Congratulations to our 5 new accredited trainers from Edinburgh City Council , Lothian NHS, Perth Kinross Council and SENSE Scotland
We had a great two days working together, exploring the Talking Mats framework and thinking about skills in terms of training and implementation of the Mats. Lots of chat but some key thoughts emerged that are worth sharing
- Keep calm with Talking Mats and have a blether
- Talking Mats gives the thinker the power to say ‘No’
- Open questions create open dialogue
- Children do but don’t get enough time to say
- Recap; Talking Mats provide a visual summary of the conversation
- It is easy to feel drowned out by other voices Talking Mats keeps the focus on the person
- It is good to have 1 to 1 time and not just when things go wrong
- The health and being resource is a perfect fit for the outcomes focused approach
There were lots of exciting ideas for future projects and further blogs which will expand on these ideas a bit more. So watch this space as the new trainers develop their ideas more.
If you are interested in becoming an accredited trainer click here
Talking Mats is fun! Whether you are sitting on the floor completing your mat or sitting at a small table, young children enjoy the fact that they can give information through multiple channels – Talking Mats is visual, auditory and tactile. It is an engaging tool to use when consulting children.They can express a view without words if they want to or they can have a conversation if they enjoy chatting. Watching a young child thinking and reflecting about where they place their symbol on the mat can be a humbling experience. Some adults still consider young children as incapable of expressing their views or opinions but in reality they can often express strong views about things and are very capable of grading their responses. Sometimes we just don’t take the time to ask them about the issues in their lives and free up some time to listen.
Talking Mats has created a specific Early years resource to make consulting young children easier. The symbols have been graded according to their developmental stage. When using the picture symbols it is important to remember:
- Most of the symbols in the Early years pack are concrete and you can quickly identify the shared meaning for example – “drawing”
- Others are concrete but have a broader meaning. An example of this is when asking about “eyes”
We have found that it is best to allow the child to interpret the meaning at their level so it maybe they have sore eyes; they don’t like their glasses or they have brown eyes. Try not to be too prescriptive when presenting the option to the child; a symbol can act as a jump off point capturing what fits for the child at the time. Just allow the meaning to emerge.
• The abstract symbols do need a bit more explanation because they ask about more complex concepts such as safety. The Early years pack asks about safety in relation to the road, physical safety and safety around others.
Asking about daily routines will give insight into how nurtured and cared for they feel. Let the child lead the discussion as much as possible.
Using visual communication is a great way to have a conversation with children in the early years and a good tool to involve children in decision making. Listening to the child’s view is essential for the GIRFEC process in Scotland and for co-producing Education Health care plans in England and Wales. Talking Mats has created a unique resource which is based on the “International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health – Children and Youth version” Talking Mats uses a framework which helps children to express themselves in a way they feel comfortable with. As adults we need to be able to facilitate the conversation.
We find that to realize the full potential of Talking Mats it is best to attend a Talking Mats course . The courses allow you to focus on your situation and how you can be creative and apply it in your own work,
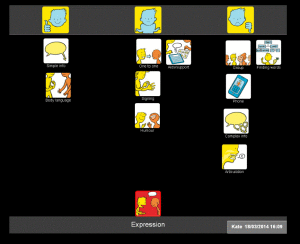
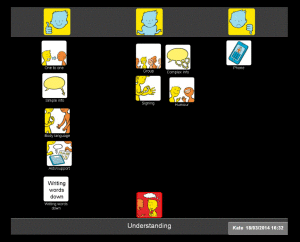
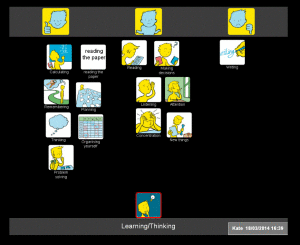
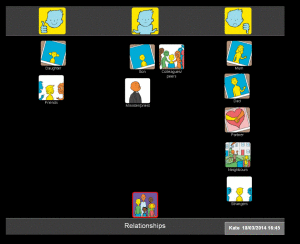
In the Health and Well-being resource, we have provided four sets of symbols to help people consider how they feel about their communication. Because communication is complex and often abstract, it can be particularly difficult for people to express their views about it, especially if they have existing communication difficulties. To make this easier, we have divided communication into four topics:
- Expression
- Understanding
- Learning and thinking
- Relationships.
In the following example, I show how each topic can be used to build up a picture of how someone feels about different aspects of their communication. I worked with Kate, a 42 year old woman who had a stroke which left her with severe expressive and receptive aphasia. She was able to communicate through vocalisations and gestures. She could sometimes draw or write down words and needed to point to ‘yes/no’ in order to reliably answer closed questions. Following discharge from hospital, I used Talking Mats with Kate to find out how she felt about her communication. I started with the ‘communication – expression’ topic and found that she felt that she was having lots of difficulties making herself understood, particularly on the phone and in group situations:
I then explored how Kate felt about understanding what people were saying to her. Kate was able to tell me that she found it easier to understand people on a one to one basis rather than in a group setting. She indicated that it really helped her if people used gestures or wrote things down. Her main difficulty was understanding people on the phone, and in fact she had stopped answering the phone altogether (see mat below).
We went on to do a mat about Kate’s learning and thinking. In this set, there are symbols which cover higher level language activities such as reading, problem solving and organisation. When we talked about these areas, Kate was able to tell me about the things she was finding most problematic, but could also identify some things that she felt she could still manage (such as calculations and reading newspapers).
I then asked Kate how she felt about communicating with different people in her life. This mat shows that Kate found talking to her husband and her parents (who lived quite far away) particularly difficult.
As a result of doing these mats, we were able to target the things that mattered most to Kate in relation to her communication, and came up with the following actions:
1. Kate felt that her husband needed support and information, so we spent time working with him, showing him the best ways to support Kate’s communication.
2. Because Kate’s parents lived quite far away, she could only contact them using the phone, which was very difficult. We worked on getting Skype set up so that Kate could communicate with her family using all the modes available to her.
By splitting communication into different sub mats, Kate was able to think about different aspects of her communication and identify the things that she found most challenging. Together we began to work out some ways to help her overcome her difficulties.
Use the communication symbols to find out what people want to work on and use a collaborative approach to establish some goals to work on in therapy. I used the original Talking Mats when I explored Kate’s communication with her, but you could do the same with Digital Talking Mats. Find out more about it here.
In a previous Blog, Joan talked about the four purposes of communication (Light 1988):
1. Expression of needs and wants
2. Information transfer
3. Social closeness
4. Social etiquette
Social closeness can often be overlooked when we support people with communication difficulties, as there can be a temptation to focus on what some see as the ‘important things’ – helping people to express their needs and wants or to transfer information. Social closeness is the glue which binds us together and helps us to form and maintain relationships. It’s really important that we establish this before we start exploring some of the difficult issues that many of the people we are working with face. In my work with people with severe aphasia, I spend time getting to know what matters to them and finding out what their interests are. This is a crucial part of building a relationship with the person and their family. It also provides a much more concrete starting point for beginning to explore rehabilitation goals, as this example shows:
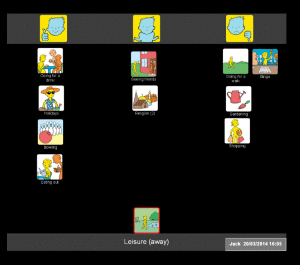
When working with Jack (a man with severe receptive and expressive aphasia), I started by using Talking Mats to ask him how he felt about leisure activities. This was a great way to get to know Jack as a person and to find out his interests. During our conversation, Jack told me that he enjoyed going out for a drink but hated shopping and bingo – and we all had a laugh as he told me this. Jack also told me that he used to like ten pin bowling. He pointed to his leg to indicate that this was something he could no longer participate in as he was now in a wheelchair. I could see that this was important to Jack, so we talked about possible ways round his physical difficulties. Jack agreed that this was something he could work on with the help of his family and the rehabilitation team.
Given that Jack had severe receptive aphasia, if I had started by using Talking Mats to identify specific problems (using a top scale of ‘managing’ and ‘not managing’) as part of the goal setting process, it is highly likely that Jack would have found this too abstract and difficult to engage in. By using the more concrete topic of leisure (with a top scale of ‘like’/’dislike’), Jack was able to reflect on his life since his stroke and tell me how he felt about his restricted physical abilities. I was also able to build up a picture of him as a person and we had fun at the same time.
When using the Health and well-being resource, think about the person you are working with in relation to the ideas and concepts that they can cope with. Exploring leisure activities is a great way to start as it means you can establish rapport by finding out what matters to them.
Have a look at this Blog to see how other people have used a topic such as leisure to build social closeness.
For those of us who work or live with people with communication difficulties it’s important that we consider the purposes of human communication. As long ago as 1988 Janice Light suggested that there were 4 main purposes and we believe this is still a good model to bear in mind.
(Light, J. (1988) “Interaction involving individuals using augmentative and alternative communication systems: state of the art and future directions”, AAC, 4, 2, 66-82)
She described these purposes as:
1. Expression of needs and want – to regulate the behaviour of another person to get something
2. Information transfer – to convey information from person A to person B
3. Social closeness – to establish and maintain relationships with others
4. Social etiquette – to conform to the social conventions of politeness
We believe that there is a tendency to concentrate too much on 1 and 2 and not enough on 3 and 4. If we dwell on needs and wants, which is very often the focus of communication aids, there is a danger that the person with the communication difficulty will find it hard to establish and/or maintain relationships.
In 1998 John Locke wrote that ‘small talk’ is crucial for the construction and enjoyment of relationships with others and that by revealing thoughts we elicit reactions from others. This is what we regard as social closeness or engagement. ‘Small talk’ or ‘social closeness’ may sound irrelevant but it is one of the most important purposes of human communication.
(Locke, J. L. (1998) “Where did all the gossip go? Casual conversation in the Information Age”, American Speech Language Hearing Association, 40, 3, 26-31)
Talking Mats, which uses attractive and motivating communication symbols, is one way to help people to express their thoughts and achieve ‘social closeness’, whether they are a 4 year old boy with Downs Syndrome or a 95 year old woman with dementia.
Talking Mats is one of the few resources that is versatile enough to be used as a stroke communication resource, for consulting children and young people or to help with communication difficulties and dementia, to name but three.
It allows people to express their thoughts in a visual way which in turn can elicit a response from their communication partner. Moreover, solid research has shown that Talking Mats increases engagement in people with different communication difficulties.
Click here to see our publications
I undertook the ‘Talking Mats’ on-line course to acquire a new skill and a way to enhance my communication with people with dementia in practice. I have found the learning strategies used are varied and interactive – so there is not a sense of sameness, even though visually there is a consistent layout to the presentation of each module (this expedites navigation). This enhances engagement and my interest so that I am never reticent in logging on to complete the next module! In the beginning, I felt that I could move a lot quicker through the course if the modules were available once each part was completed, instead of having to wait for feedback on each assignment. However, nearing the end of the training course, the benefits of this approach are now clearer. Spaced learning and spaced practice allows for thinking time and internalisation of the module components. In this way, I have come to appreciate the part skills involved in the overall process and how they come together. I now find myself observing the skills involved and the reactions of all communicating as well as the surrounding environment, body language etc. I have also found myself looking back over the past module materials to ensure I am integrating as I go and to remind myself of the rationales for the actions that need to be taken, as well as ensuring that I am more and more familiar with the new terminology that I have been exposed too.
Little did I know when I signed up that the benefits of learning about and how to use ‘Talking Mats’ would stretch wider than what I initially anticipated or wanted! In completing the course, I am now much more aware of my communication practice in general, and the part-skills involved. I can also now see the wide applicability of ‘Talking Mats’ to different populations, age groups and conditions. Communication is everywhere but it needs to be efficient and effective – I am now more confident that my communication practice will improve as a result of this course. For me this is the best outcome possible.
Please click here to find out how to book on the next course
Guest Blog by Ruth Cape
Ruth is Lois Cameron’s daughter and she has contributed the following guest blog about her recent experience of taking and passing her driving test and how using a Talking Mat the night before her test developed a nerve controlling action plan!
My Driving test -a nerve wracking prospect
Even the simplest of actions within the context of a nerve-wracking event can be magnified to stomach churning proportions. The thought of opening a car door and putting on a seatbelt has never before given me much trouble. Now suddenly I’m imagining fumbling with the handle, not finding the seatbelt lock – or worse, forgetting the thing altogether; while trying to look cool and collected in front of a reportedly ‘no-benefit-of-the-doubt’ driving test examiner. It was the night before my practical driving test. I had recently failed on a nerves-getting-the-better-of-me manoeuvre and knew I’d be unlikely to get another test for 3 months if this one didn’t work out. I live on the Isle of Harris. Winter gales make cycling difficult, if not often impossible. Winter busses are sporadic. My housemate-cum-chauffeur-cum-co-driver had just left the island. My driving lessons in Stornoway required a four hour round trip. To put it lightly, I was pretty keen to pass. If I’m honest, even if I knew I could get another test the next week and if my day to day life wouldn’t be much effected by the use of a car, simply the thought of 40 minutes in that vehicle-turned-pressure-cooker, every move scrutinised by a stranger in a high-vis would have given me the tangled stomach I suffered from that test eve.
Talking Mat trialled as a pre-driving test nerve-gatherer
Timing was on my side this time round; my mum – Lois – and her colleague – Sally – happened to be on a Talking Mats training visit to Stornoway that pre-test day. Finished with a day of training, we met for dinner and, as plates were cleared away and calming herbal tea was ordered, out came the pen, paper and post-it notes. This – I gather – was the first Talking Mat trialled as a pre-driving test nerve-gatherer; proving just how versatile a tool it is. With a top-scale to gauge my confidence levels, different aspects of the test were handed to me and ended up in a cluster around the lower two steps of the scale; opening the door and putting on my seatbelt sat just a little above parallel parks and three point turns. While this mostly went to show that it was the whole experience that was knotting my insides, it allowed a valuable opening for discussion on how to go about unknotting, or at least concealing the knots.
Reframing thoughts and strategies for success
Re-framing the nerves to focused adrenalin, positive mantra, power posing and deep breaths – the mediation of the Mat provided the opportunity to work through strategies for success. I went to bed, glad – at least – to have had something to do to that evening to channel the nervous energy. The following morning I opened that car door, put on my seatbelt and proceeded to pass with one minor. Now, I can’t allow Talking Mats to take all the credit for this turn of events, but I can definitely praise the tool and thank my two informal practitioners for keeping me focused. From this experience, I’m sure there is potential for a wider Talking Mats scope for tackling anxiety and for use in relation to stressful situations.
Now Harris has opened up, and I’m off to explore…
The following are thoughts from Jenni, a Psychologist who attended the Talking Mats Accredited training course.
‘Meeting with five colleagues from Sweden, England and various parts of Scotland for the accredited Talking Mats Training this month has been a fascinating experience. I have been accustomed to using Talking Mats with children and young people over the past seven years, and have seen the value of the approach in helping young people give their views for a meeting – particularly if they have communication difficulties and would struggle either through lack of confidence or skill to speak out when others are present.
However, we were not just a group who work with children and young people. Most came from health settings and examples were drawn from elderly patients, some with dementia, others with autism. As we shared our videos and told our stories it was obvious to me how relevant Talking Mats can be in those settings too. Some of the stories shook me. One person told how she was deep in conversation with a lady over her Talking Mat when the tea lady burst in, poured a cup of tea for the resident, asked if she was having a good time playing at puzzles, then left before any answer could be given. Time and again we found ourselves asking what is it about our institutions that puts routines above real communication and above proper respect for an individual.
In preparing a video to bring to the training I undertook a Talking Mat with my father, who is almost 90. It was a new kind of conversation for us both, but we were surprised – the structure allowed us to talk about what was going well and what needed a bit of an adjustment in domestic life and we both learned from the conversation. I think we will do it again!
Indeed, at one stage in the training we were asked to dream big and look at how we might want to take use of Talking Mats into new areas. I identified some good friends – one 91, one 101 and one 104 – where conversation can become rather one-sided. I am interested in the power of Talking Mats to help create a genuine dialogue when these friends are reminiscing, in other words, to help me to be not just a listener but to enter the dialogue. Having a record of the conversation will help us take the discussion further when we return to it.
As ever, the time spent with Talking Mats colleagues was refreshing, stimulating and I can’t wait to go home and try out some new ideas!’
Jenni Barr, Educational Psychologist
Attending one of our standard training courses will:
- Provide you with a range of practical tools and models that will help you evaluate a person’s ability and their level of support required
- Give you a holistic framework to support people with communication disability
- Build your confidence in using Talking Mats
- Encourage your creativity in using and applying Talking Mats in different situations such as goal setting, sharing views, supporting disclosure, enabling decision making…..the list is endless!
You can either
- Book places on our regular courses held in different venues across the UK
- Book a bespoke training for your organisation
- Participate in our 12 week online training course
However, you cannot train others unless you have completed and passed one of our residential ‘train the trainers’ courses. We put significant emphasis on our accredited training because without it, the quality and integrity of the Talking Mats framework is diluted and damaged.Talking Mats is based on extensive research and although it may appear simple, there are many complex layers involved in using it and we need to be confident that trainers have an in depth knowledge and understanding of these.
In order to apply to become a Talking Mats trainer you have to have completed the standard training (above), be experienced in using Talking Mats and fulfil the course requirements.
Intellectual Property
Talking Mats was originally developed at University of Stirling and the Intellectual Property is held by the University and Talking Mats Limited is assigned the sole rights to Talking Mats. Talking Mats is registered as a trademark. Only training that is sanctioned by us is recognised and anyone training others without being a recognized Talking Mats trainer is infringing Intellectual Property and copyright.
Signposting and sharing knowledge
We are of course delighted when people share their knowledge and experience of Talking Mats and signpost others to the website and resources.
 Online training login
Online training login